Data collection and analysis has the power to make huge inroads in the field of medicine, from AI-assisted diagnoses, to digitalization reducing the burden on administrators. But medical information is some of the most sensitive data out there, that demands especially careful management. In 2023, Thoughtworks, as part of the Bahmni Coalition, partnered with SNOMED International to enhance Bahmni’s support for SNOMED CT and ensure privacy and accuracy in the bulk handling of electronic medical records (EMR).
Bahmni is an open-source hospital information and EMR system that Thoughtworks created and has nurtured since 2012. It’s often deployed in low-resource settings, to improve data management and access, and by extension, standards of care. SNOMED International is a not-for-profit organization that determines global standards for health terms.
Thoughtworks and SNOMED International came together to develop an open-source module of SNOMED CT (a clinical terminology dictionary) that would integrate with the Bahmni EMR, making standardized clinical terminology available to its users. Critically, it would enable clinicians and organizations at the early stages of digital health maturity—those still capturing data using free text, radio buttons, or simple value lists—to develop their data capture and retrieval methods, moving up the digital health maturity model.
For instance, see this screenshot of Bahmni Clinical Diagnosis entry screen, that shows SNOMED CT search results for the term “Asthma”:
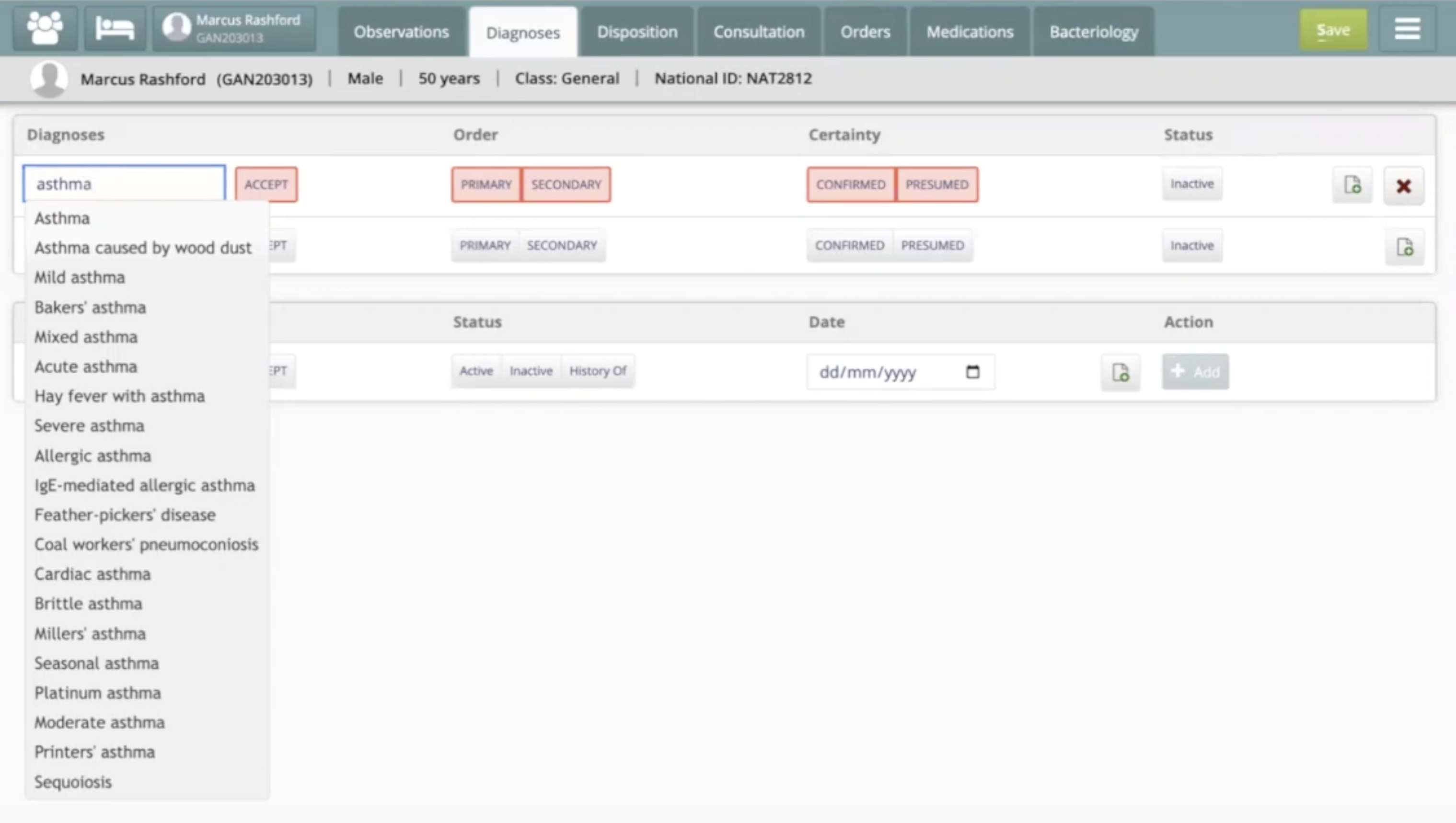

The Bahmni-SNOMED CT integration now means providers can search for and save diagnoses and clinical data, generate reports, create forms, and access clinical decision support use-cases. They can also receive alerts when a drug-diagnosis interaction is contraindicated.
Here’s an example contraindication alert:
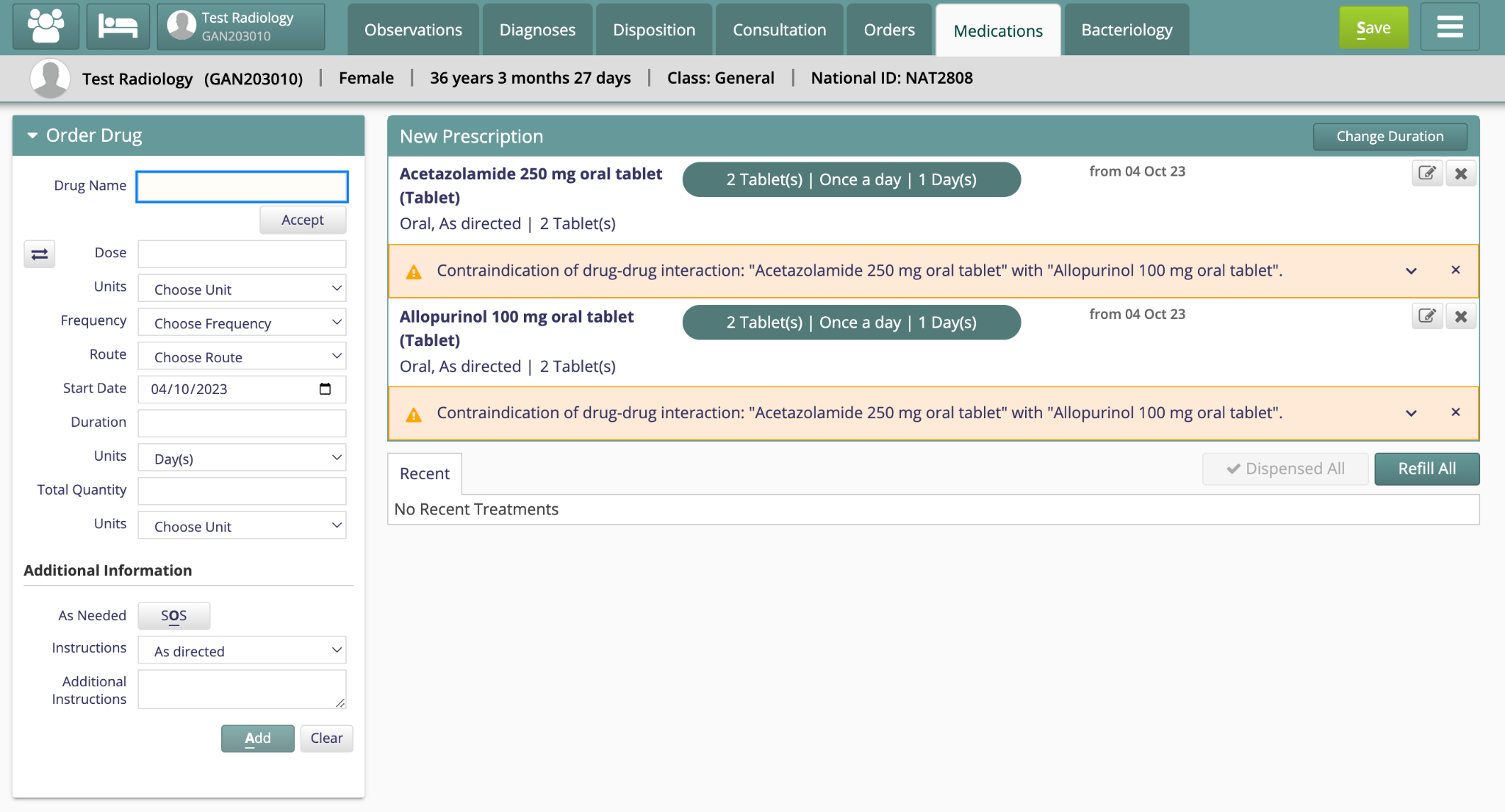

As part of this initiative, one of the requirements was for Bahmni to be able to bulk export patient data for analytics purposes in an NDJson/FHIR format, which can then be loaded into the open-source SNOMED Analytics tool. Integration with the tool enables Bahmni adopters to leverage the SNOMED CT ontology for analytics and research. Users can make meaning-based selections across patients to generate practical insights, for example, to measure correlations between different treatment options and various patient outcomes.
Responsible tech: Keeping privacy front and center
Thoughtworks also wanted to ensure that, by default, any bulk patient data export should be anonymized with no personally identifiable information (PII) data sent over.
Furthermore, the exports would sometimes need flexibility of data for analytics purposes—for instance, patient gender may be needed but not age, or simply the year rather than exact date of birth. Such flexibility was therefore built into how the data exports / anonymization algorithm should work to cater for various use cases.
The Bahmni team introduced a configuration-based anonymization mechanism (see example) that allowed Bahmni administrators to choose the degree of anonymization they wanted to offer out-of-the-box. Various access controls were also introduced so that one could either disallow bulk export or non-anonymized export etc. to provide granular authorization-based control to this feature.
The Snomed International-Thoughtworks collaboration marks a step change for Bahmni, enhancing the clinician’s tooling: ultimately improving the accuracy, consistency and speed of patient care.
Disclaimer: The statements and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the positions of Thoughtworks.















